Publications
- All
-
Following
You must log in
before getting
tailored content. -
Interests
You must log in
before getting
tailored content. - Most liked
- Most viewed
What Is Abdominal Pain?
If you’re suffering from abdominal pain in Manhattan or one of the other boroughs, it can be a mild inconvenience treatable with over-the-counter remedies or a sign of a severe illness that requires immediate attention from a gastroenterologist.
Abdominal pain should always be evaluated with a thorough consultation and examination by a gastroenterologist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan, as it may be a symptom of a severe illness or condition. There are multiple causes of stomach pain that should be investigated by a top GI specialist. Abdominal pain can be acute or chronic, and it can result from problems with the stomach, appendix, gallbladder, spleen, bowel, liver, or gynecological issues.
Therefore, it is critical that you see our practice’s doctor for an examination and further investigation to determine the source of your pain. If you’re experiencing abdominal pain in the Upper East Side, your problem deserves to be addressed by a best-in-class gastroenterologist.
Read more:https://www.manhattangastroenterology.com/conditions/abdominal-pain/
Working Hours:
Monday: 7:30 am - 7:00 pm
Tuesday: 7:30 am - 7:00 pm
Wednesday: 7:30 am - 7:00 pm
Thursday: 7:30 am - 7:00 pm
Friday: 7:30 am - 7:00 pm
Saturday: CLOSED
Sunday: CLOSED
Payment: cash, check, credit cards.
Manhattan Gastroenterology
80 Maiden Ln, Suite 1204B
New York, NY 10038
(646) 813-2095
https://www.manhattangastroenterology.com/gastroenterologist-downtown-financial-district/
Location on the map:
https://maps.app.goo.gl/xXW8HAq2qUFeaX2d8
https://plus.codes/87G7PX4R+RV
Nearby Locations:
Lower East Side | Chinatown | Battery Park City | Soho | Tribeca
10038, 10002, 10003, 10004, 10009, 10012, 10013, 10014
Directory:
Tags:

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
Directory:
Tags:

What Is an Eye Emergency?
Emergency Eye CareAn eye emergency refers to any sudden or severe eye issue that demands prompt attention from an emergency eye doctor. These emergencies encompass eye injuries, unexpected visual changes, intense eye pain, foreign objects in the eye, chemical exposure, and the sudden appearance of flashing lights or floaters. Conditions such as conjunctivitis, characterized by pain, redness, and discharge, can also lead to an eye emergency.
Upon your visit, the emergency optometrist conducts a thorough examination to assess the type and severity of the issue. This evaluation may involve using specialized equipment, such as a slit lamp, to detect any eye injuries or abnormalities. Treatment options, including medications, eye drops, irrigation, patching, or surgical procedures, depend on the findings.
If you require an emergency eye doctor in Manhattan, consider seeking care from the family eye experts at Eye Physicians in NYC. They offer treatment for both adults and children at their walk-in eye clinic in NYC.
Emergency Eye Care Near Me: Alleviate Your Pain and Preserve Your Vision
When dealing with an injury that affects your eye or causes sudden changes in vision, whether it’s a foreign object, chemical exposure, or other serious conditions, seeking prompt medical attention is essential. Choose an ophthalmologist or optometrist who is available promptly, especially during off-hours or weekends, and has experience in diagnosing and managing eye emergencies like central retinal artery occlusions, chemical injuries, and retinal detachments.
How to Find a Doctor Offering Emergency Eye Care in Your Area
If you’re looking for an emergency eye doctor nearby, here are a few tips:
- Reach out to friends and family for recommendations.
- Search online for “emergency eye care near me,” “emergency eye doctor near me,” and “24 hour emergency eye care near me.”
- Read reviews of local emergency eye doctor online and schedule consultations with them to get to know their practice.
Recognized worldwide as leaders in the field, the ophthalmologists and optometrists at Eye Physicians are more than capable of diagnosing emergency eye problems and offering solutions. We will provide you with the best treatment for your needs to help ensure you have a safe and speedy recovery.
Eye Physicians
110 Lafayette St, Suite 503
New York, NY 10013
Office Tel: (212) 292-4814
Fax: (212) 628-0698
Web Address: https://www.myeyephysicians.com/
Our locations on the map: https://maps.app.goo.gl/pkDgr4UdoZSScuaR7
https://plus.codes/87G7PX9X+8M New York, USA
Nearby Locations:
Lower Manhattan | Little Italy | Chinatown | Civic Center | Tribeca | SoHo
10013 | 10012 | 10007 | 10002
Working Hours:
Monday: 8 am–5 pm
Tuesday: 8 am–5 pm
Wednesday: 8 am–7 pm
Thursday: 8 am–5 pm
Friday: 8 am–5 pm
Saturday: 8 am–5 pm
Sunday: Closed
Payment: cash, check, credit cards.
Directory:
Tags:
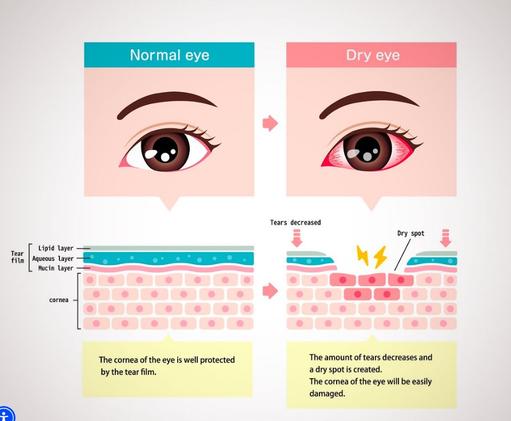
Dry eyes can be uncomfortable, as they make reading and other activities tiresome and difficult. Without the appropriate dry eye syndrome treatment, you may develop worse complications that permanently affect your vision. Call the best dry eye syndrome specialists in New York City at Eye Physicians. They know how to provide you with a diagnosis and effectively treat dry eye syndrome, helping you avoid further complications. They work hard to get you in and out of the office in under an hour. So you have no excuses; start treating dry eye syndrome the right way now.
What Are the Best Dry Eyes Treatment Options?
The best dry eye treatment for you depends on the severity of the problems and the cause. For an occasional bout of dry eyes that’s not too bothersome, your eye doctor may recommend over-the-counter eye drops.
For more serious dry eye, a dry eye doctor near me in New York City may prescribe dry eye treatments such as:
Prescription eye drops, containing steroids or other medications
Eyelid surgery, in rare instances, a lower eye lid is too loose, and the tears drain too quickly
Punctal plugs, placed in the ducts in the inner corner of your eyes to keep the tears from draining as quickly
The treatments are as individual as you are. If you’re having eye problems in Downtown Manhattan, you need the best dry eye treatments you can find. Contact Eye Physicians for the most accurate diagnoses and effective dry eye treatments in addition to treatment for a wide range of conditions.
Eye Physicians
110 Lafayette St, Suite 503
New York, NY 10013
Office Tel: (212) 292-4814
Fax: (212) 628-0698
Web Address: https://www.myeyephysicians.com/
Our locations on the map: https://maps.app.goo.gl/pkDgr4UdoZSScuaR7
https://plus.codes/87G7PX9X+8M New York, USA
Nearby Locations:
Lower Manhattan | Little Italy | Chinatown | Civic Center | Tribeca | SoHo
10013 | 10012 | 10007 | 10002
Working Hours:
Monday: 8 am–5 pm
Tuesday: 8 am–5 pm
Wednesday: 8 am–7 pm
Thursday: 8 am–5 pm
Friday: 8 am–5 pm
Saturday: 8 am–5 pm
Sunday: Closed
Payment: cash, check, credit cards.

Dolce MD in Laguna Beach, CA, brings a personalized touch to healthcare with our concierge doctor services, tailored to the unique needs of Orange County residents. Emphasizing a close patient-physician relationship, we offer comprehensive care that extends beyond the traditional office visit. Our clients enjoy direct access to their family doctor for consultations, ensuring prompt attention and peace of mind. Whether you're seeking IV therapy in Dana Point or general medical advice, our practice is dedicated to maintaining your wellness with a holistic approach. Our concierge medicine service caters to the communities of Laguna Beach, Newport Beach, and Dana Point, providing an elevated healthcare experience that prioritizes your time and well-being.
Address: 310 Glenneyre St, Laguna Beach, CA, 92651
Phone: 949 209-9266
Directory:
Tags:

|
|
|
|
|
Directory:
Tags:
Who Should Consider Cosmetic Dentistry?
Do you cover your mouth when talking to others or feel embarrassed to smile or laugh because your teeth don’t look their best?
Cosmetic dentistry can help, from treating minor imperfections to larger and more complex smile makeovers.
Treatment is worth considering if you have the following problems:
- Chipped or cracked teeth
From safe, effective teeth whitening to complete smile makeovers, we can help you achieve your dream smile.
- Gaps between teeth
From safe, effective teeth whitening to complete smile makeovers, we can help you achieve your dream smile.
- Teeth slightly overlapping
Teeth that are slightly overlapping or not quite perfectly straight From safe, effective teeth whitening to complete smile
- Teeth ideal shape contour
Teeth that are a less-than-ideal shape, size, or contour From safe, effective teeth whitening to complete smile
- A gummy smile
Teeth that are slightly overlapping or not quite perfectly straight From safe, effective teeth whitening to complete smile
- Stained teeth
Teeth that are a less-than-ideal shape, size, or contour From safe, effective teeth whitening to complete smile.
Google Maps: https://maps.app.goo.gl/oksyfTuQodLzAix68
https://plus.codes/87G7VWWW+8X
Nearby Locations & Municipalities:
Maywood | Teaneck | Lodi | Little Ferry | Ridgefield Park | Hasbrouck Heights | River Edge | Saddle Brook | Palisades Park | New Milford | Garfield | Englewood | Bergenfield | Ridgefield | Elmwood Park
Nearby Zip Codes
07601 | 07602 | 07603 | 07604 | 07666 | 07644 | 07643 | 07660 | 07657 | 07661 | 07663 | 07663 | 07650 | 07646 | 07631 | 07632 | 07621 | 07657
My New Jersey Dentist
385 Prospect Ave, Suite 304,
Hackensack, NJ 07601
(201) 425–9580
Web Address: https://mynjdentist.com/
Working Hours:
Monday-Friday: 10:00 am — 6:00 pm
Saturday: 9:00 am — 3:00 pm
Sunday: by appointment only
Payment: cash, check, credit cards.















